Video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS)
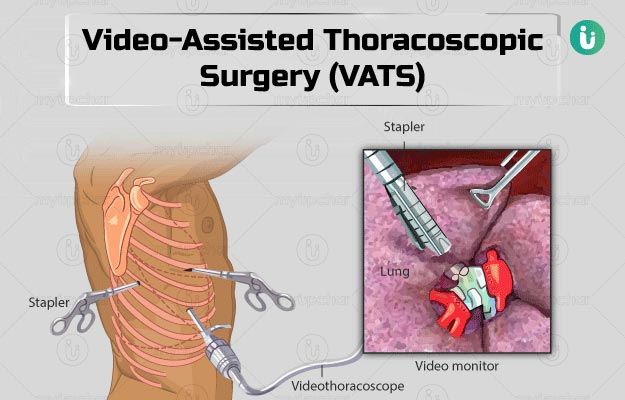
Video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS) is a surgical procedure used in the chest and lungs. It is a type of 'keyhole' surgery where only very small incisions are made to the body. VATS uses a special instrument called a thoracoscope. This is a thin, tube-like instrument which has a camera built into the end. The camera feeds pictures from the chest on to a screen. This allows your surgeon to look inside the chest and lungs.
Procedure
The surgeon makes two or three small incisions in the chest wall near the ribs. These holes are known as ports and are usually about two cm long.
The surgeon then inserts the thoracoscope through one hole. The camera in the thoracoscope feeds video images to a computer screen, allowing the surgeon to see inside the chest.
The surgeon will also insert special surgical instruments into the other incisions. These instruments can be used to remove tissue which may have been seen on an X-ray, or fluid found in the chest.
Once the surgery has finished, the instruments are removed and the incisions are closed, usually with stitches.
Advantages
- Minimal postoperative pain
- Shorter hospital stay and early return to work and normal activities.
- Excellent cosmetic results.
VATS is used in both diagnostic and therapeutic pleural, lung, and mediastinal surgery. Specific indications include the following:
Stapled lung biopsy: A lung biopsy removes a small piece of lung tissue that can be looked at under a microscope by the pathologist or sent to a microbiological laboratory for culture to identify the organisms causing a disease.
Lobectomy or pneumonectomy: Pneumonectomy is a surgical procedure in which an entire lung is removed. Lobectomy is a common surgical procedure that removes one lobe of the lung that contains cancerous cells
Resection of peripheral pulmonary nodule
Evaluation of mediastinal tumors or adenopathy: Mediastinal tumors are benign or cancerous growths that form in the area of the chest that separates the lungs. Adenopathy is the enlargement of lymph nodes anywhere in your body.
Pleural biopsy: A pleural biopsy is a procedure in which a sample of the pleura (the membrane that surrounds the lungs) is removed with a special biopsy needle or during surgery to determine if infection, cancer, or another condition is present.
Bullectomy: Bullectomy is the surgical removal of a bulla, which is a dilated air space in the lung parenchyma measuring more than 1 cm.
Treatment of recurrent pneumothorax: A pneumothorax refers to a collection of air in the pleural cavity (between the lung and the chest wall) resulting in collapse of the lung on the affected side.
Management of loculated empyema: Empyema is a collection of pus (dead cells and infected fluid) inside a body cavity.
Pleurodesis of malignant effusions: Pleurodesis is a well-accepted, palliative therapy for patients with recurrent malignant pleural effusion.
Repair of a bronchopleural fistula: A bronchopleural fistula is a communication between the pleural space and the bronchial tree.
Chest trauma (mainly diaphragmatic injuries)
Pericardial window: A pericardial window is a cardiac surgical procedure to create a fistula - or "window" - from the pericardial space to the pleural cavity.
Sympathectomy: Sympathectomy is a surgical procedure that destroys nerves in the sympathetic nervous system.
Truncal vagotomy: Vagotomy is an essential component of surgical management of peptic (duodenal and gastric) ulcer disease (PUD).
Thymectomy: Thymectomy is an operation to remove the thymus gland. Thymectomy is usually indicated when thymoma are present in the thymus.

Dr Shashikiran N J
MBBS, MS, MCh
Lead Consultant Minimally Invasive Thoracic surgery
Apollo Hospitals Hyderabad
